Paper
- PDF: https://proceedings.mlr.press/v70/gilmer17a/gilmer17a.pdf
- ICML 2017 presentation: https://youtu.be/NJEb5sqjv2w?si=97Blra9en7BB-Tqa
- Paper with code: https://paperswithcode.com/paper/neural-message-passing-for-quantum-chemistry
- Keras code(Keras tutorial): https://keras.io/examples/graph/mpnn-molecular-graphs/
- Citations: 6282
Abstract
- 기존의 message passing algorithm → aggregation 과정을 Message Passing Neural Network(MPNN) 이라는 일반화된 framework로 재구성하여 활용성을 증대시켰음
1. Introduction
- 타 분야와 달리 machine learning을 통해 분자, 물질들의 물성을 예측하는 일은 여전히 어려움을 겪고 있음.
- 대부분의 연구들은 feature engineering에 맴돌고 있고, NN을 사용하는 경우는 흔치 않다.
- 적절한 inductive biases(유도 편향?)을 가진 모델(GNN)을 찾을 수 있다면 ML을 적용할 수 있을 것이다.
- 최근 quantum chemistry calculation과 molecular dynamics simulations와 관련된 굉장히 많은 데이터가 생성있음.
- 원자 시스템의 대칭성, 그래프의 동형성(isomorphism)에 불변한 GNN은 분자에도 잘 적용될 것이다.
- 본 논문의 목표는, chemical prediction 문제에 사용할 수 있는 ML 모델을 설명하는 것이다.
- 해당 ML 모델은 분자 그래프의 feature들을 직접 사용하고, 그래프 동형성에 불변함.
- 이를 위해, 기존 GNN 모델들에 대한 일반화(
abstracts the commonalities)인 Massage Passing Nueral Networks (MPNNs)라 불리는 supervised learning framework를 소개한다. - 해당 framework를 기반으로 application에 따른 적절한 변형만 제안하는 것이 좋을 듯.
- 본 논문의 application은 작은 유기분자들에 대한 quantum mechanical properties를 예측하는 작업이다.(
Figure 1)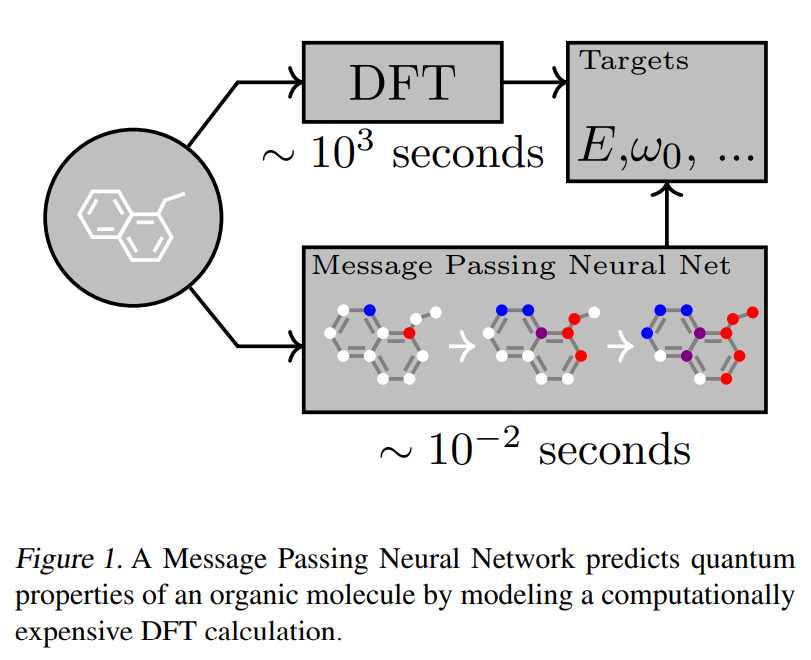
- QM9 dataset을 벤치마크로 하여 진행한다.
- QM9 데이터 구성: 130k개의 분자에 대해 13개의 물성(DFT로 측정, DFT: quantum mechanical simulation method)을 예측하는 regression task.
- QM9 예측을 잘할 수 있다면, 파급효과가 크다.
- ??? (QM9에 대한 설명인 듯)
QM9 therefore lets us consider both the setting where the complete molecular geometry is known (atomic distances, bond angles, etc.) and the setting where we need to compute properties that might still be defined in terms of the spatial positions of atoms, but where only the atom and bond information (i.e. graph) is available as input. In the latter case, the model must implicitly fit something about the computation used to determine a low energy 3D conformation and hopefully would still work on problems where it is not clear how to compute a reasonable 3D conformation.
-
13개의 물성에 대하여 화학 커뮤니티에 의해 정밀하게 만들어진 target 오차(
chemical accuracy)를 줄이는 것을 목표로 한다. - MPNN family의 새로운 변형을 통해, QM9 에서 SOTA를 찍고, 2개를 제외한 모든 target에서 chemical accuracy 내에서 DFT 계산을 예측할 것이다.
- 주요 기여는 다음과 같다.
- 13개 target에 대해 SOTA를 찍었고, 11개 대상에서 chemical accuaracy 내에서 DFT를 예측하는 MPNN을 개발.
- 분자의 위상 정보 없이 분자의 토폴로지만을 입력으로 사용하면서 5개 target에서 chemical accuaracy 내에서 DFT를 예측하는 MPNNs를 개발.
- MPNNs를 학습하는 효율적인 일반적인 방법론을 개발.
- MPNN과 application을 잘 보고 잘 적용해라
2. Message Passing Neural Networks
- MPNNs의 forward pass는 2개의 phases를 가진다.
- Notation
- $G$: undirected graphs
- $x_v$: node features
- $e_{vw}$: edge features
- Message passing phase
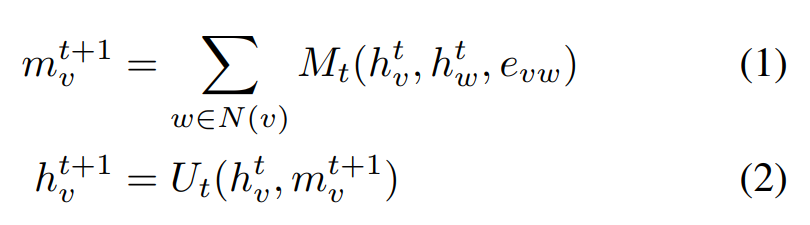
- Message passing phase
- $T$번 message functions $M_t$ (learnable)를 반복
- Vertex update function $U_t$ (learnable)를 수행
- $m_v$: message at node $v$
- $h_v$: hidden states at node $v$
- Readout phase
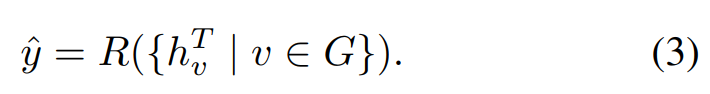
- Readout phase
- 그래프에 대한 feature vector를 계산하는 과정
- Readout function $R$ (learnable)를 node의 hidden states에 적용
- $R$은 permutation invariant 해야한다.
- 결국 $M, U, R$을 무엇으로 할 지 결정하면 되는 것.
- Edge features($h_{e_{vw}}$)도 node features($h_v$)와 마찬가지로 같은 phase를 통해 업데이트할 수 있음.
- Notation
- Family: Convolutional Networks for Learning Molecular Fingerprints
- $M(h_v, h_w, e_{vw}) = (h_w, e_{vw})$
- $(.,.)$: concatenation
- $U_t(h^t_v, m^{t+1}_v) = \sigma(H^{deg(v)}_t \ m^{t+1}_v)$
- $\sigma$: sigmoid function
- $R = f\big( \sum_{v,t} \text{softmax} (W_t h^t_v) \big)$
- $f$: NN
- 모든 hidden states $h^t_v$ 마다 skip connection이 적용
- $M(h_v, h_w, e_{vw}) = (h_w, e_{vw})$
- Family: Gated Graph Neural Networks (GG-NN)
- $M(h_v, h_w, e_{vw}) = A_{e_{vw}} h^t_w$
- $A_{e_{vw}}$: learned matrix
- $U_t = GRU(h^t_v, m^{t+1}_v)$
- Weight tying을 사용하여 각 time step $t$ 마다, update function $U_t$를 공유한다.
- Readout function
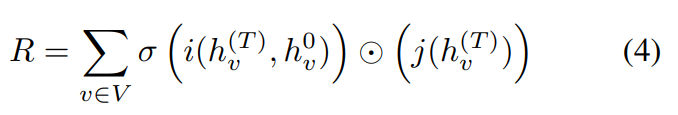
- $i, j$: NN
- $\odot$: elementwise multiplication
- $M(h_v, h_w, e_{vw}) = A_{e_{vw}} h^t_w$
- Family: Interaction Networks 등에 대한 설명
3. Related Work
4. QM9 Dataset
5. MPNN Variants
-
GG-NN(Gated Graph Neural Networks)이 괜찮은 baseline이라 이것을 기반으로 MPNNs을 만들어간다.(
our MPNN model, 이하 MPNN) - Remarks
- $d$: dimension of the internal hidden representation of each node
- $n$: the number of nodes in the graph
- 구현하는 MPNNs는 일반적으로 directed graphs에서 작동하는 것을 가정하지만, undirected인 경우, 같은 label을 가진 incoming, outcomming edge로 나누어주면 된다.(message channel: $d \rarr 2d$)
- MPNN의 input 구성
- $x_v$: 그래프 내 node들에 대한 feature vectors
- $A$: 분자 내 다른 bond들을 구분하고, 원자간 거리를 알려주는 adjacency matrix
- $h^0_v$: $x_v$를 $d$ 차원으로 패딩하여 초기화
- Time step $t$에서 사용되는 모든 weight들은 tying이고 GG-NN처럼 GRU를 사용하여 update
5.1 Message Functions
- Matrix Multiplication (for node features)
- $M(h_v, h_w, e_{vw}) = A_{e_{vw}} h_w$
- Edge Network (for edge features)
- $M(h_v, h_w, e_{vw}) = A(e_{vw}) h_w$
- $A(e_{vw})$: edge vector $e_{vw}$를 $d \times d$ matrix로 매핑하는 NN.
- $M(h_v, h_w, e_{vw}) = A(e_{vw}) h_w$
- Pair Message
- Matrix multiplication rule의 한 가지 특성으로 message를 node $w$에서 $v$로 보낼 때, node $v$의 hidden state $h_v$가 고려되지 않는다는 점이 있는데 이는 비효율적이다.
- 즉, node message가 source, destination node 모두에 종속될 때 network가 message channel을 더 효과적으로 사용할 수 있다.
- 최종적으로, $m_{wv} = f(h^t_w, h^t_v, e_{vw})$ ($f$: NN)
- Direction이 있음을 주의하여 사용.
5.2 Virtual Graph Elements
- 연결되지 않은 node pair에 “virtual” edge type을 추가하면 propagation phase에서 먼 거리로 정보를 전달할 수 있게된다.
- 데이터 전처리 과정에서 수행.
- Latent “master” node를 사용하는 것도 실험해보았음.
- 모든 node에 special edge type으로 연결된 “master” node를 추가한다는 것.
- Master node는 모든 node들이 매 step 마다 읽고 쓸 수 있는 global scratch space로 사용된다.
- Master node는 다른 차원인 $d_{master}$ 차원을 가지고 있고 internal update function(GRU) 역시 다른 weight를 가진다.
- 마찬가지로 이런 작업은 정보가 멀리 갈 수 있도록 도와준다.
5.3 Readout Functions
2가지 readout function을 사용해보았음.
-
GG-NN에서 사용한 readout function
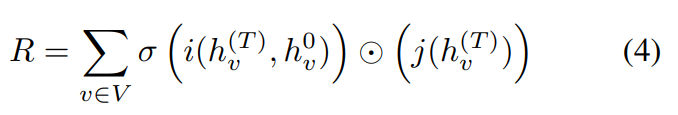
-
Set2set model
- 각 tuple $(h^T_v, x_v)$에 대하여 linear projection을 수행.
- Projected tuples $T = {(h^T_v, x_v)}$를 input으로 사용.
- $M$ steps 계산 후에, set2set model이 graph level embedding $q^*_t$를 생성.
- Tuple $T$의 순서와 무관하게 동일한 $q^*_t$가 생성되야함.
5.4 Multiple Towers
- Dense graph에 대한 message passing phase의 한 step은 $O(n^2d^2)$ float point multiplication을 요구할 정도로 무겁다.
- 이 문제를 해결하기 위해, $d$ 차원 node embeddings $h^t_v$를 $k$개의 $d/k$차원으로 나눈다. ($h^{t,k}_v$)
- …
…
8. Results
- Target 마다 모델을 따로 만들어서 학습시키는 것이 더 우수한 결과를 보여주었다.
- 최고 성능의 MPNN은
- Message function: Edge network
- Readout function: set2set
- Explicit hydrgens
- Ensemble 5
PREVIOUSEtc